Faults and Protection
Faults
causes leading to disturbances
unintended circuit interruption, broken conductor
overload: load currents exceed rated values of the equipment (lines, transformers)
overload tripping of line may result in overloads of other lines (cascading overload tripping)
unintended connection between conductors of different phases => short circuit
unintended connection between phase and ground => earth fault
low impedance grounding of the transformer neutral
=> short circuit, must be switched off by the protection immediately
isolated transformer neutral => earth fault, disconnection not necessary
earth fault compensation, reactance between transformer neutral and earth reduces earth fault current
not necessary to switch off earth fault, continuous service with earth fault
phase to ground voltages during earth fault: faulted phase 0 V, healthy phases nominal x sqrt(3)
system with earth fault can be operated for one or two hours,
but risk of double earth fault because of increased voltage in healthy phases
fault types
three phase short circuit, symmetrical
two phase, phase to phase short circuit
two phase short circuit with ground
earth fault
during fault: abnormal current and voltage conditions
permanent faults
temporary faults
arc extinguishes, faults removed by deenergizing the faulted equipment
connection of transformer neutral
transformer neutral
low impedance grounding
isolated transformer neutral
peterson coil, earth fault compensation
low impedance grounding (EHV, HV, (MV)
earth fault => short circuit, must be switched off immediately
disadvantage: high fault currents, service interruption
advantage: defined fault location, faulted line is tripped
isolated transformer neutral (special cases: industrial plants, mines)
earth fault => no short circuit, earth fault current only because of line capacitance, continued operation
earth fault must be found and can be switched off without consumer interruption
phase to ground voltage of healthy phases => phase to phase voltage
advantage: no interruption of service for single earth fault, low fault currents
disadvantage: high voltage (sqrt(3) x UN) in healthy phases of all lines, difficult to find
earth fault compensation HV, MV
earth fault current further reduced by reactance between transformer neutral and ground
Protection
objectives of protection schemes
prevent damage of equipment
clear short circuits as quick as possible
extinguish arc
prevent expansion of a disturbance
maintain continuous supply to customers
limit fault to an area as small as possible
smallest possible area to be disconnected
restore supply quickly
principles of protection schemes
selectivity
switch off the minimum possible part of the network
clear fault as quick as possible
< 100 ms (first time zone of distance protection) up to a few seconds (overcurrent relay)
burning arc causes damage
protection range
time step shall cover max. area
reliability
backup protection
time zones
protection devices (relays)
Overcurrent Protection
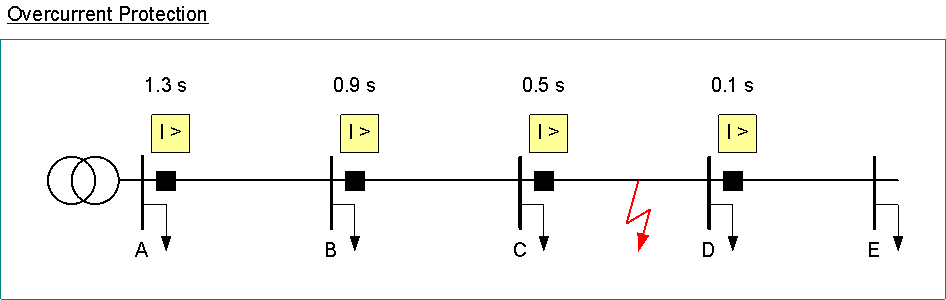
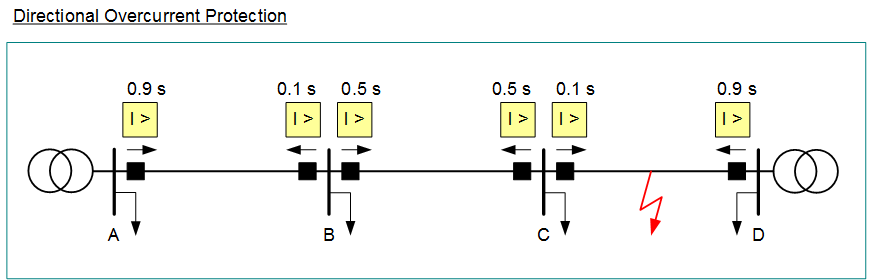
overcurrent protection > I
used in medium and low voltage networks
protection against short circuits and overloads
overcurrent relays (medium and low voltage)
current measurement
circuit breaker receives tripping signal from over current relay
fuses (medium and low voltage)
conductor melts, if current is above rated current
cheap
reclosure: replace fuse (no remote control)
additional load disconnector required
selectivity by increasing delay
=> disadvantage: longest delay for faults near injection where the short circuit current is highest
Distance Protection
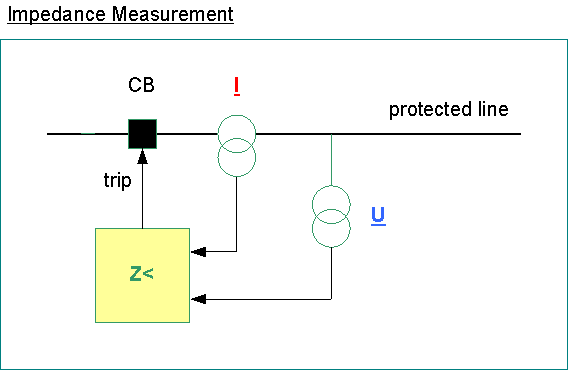
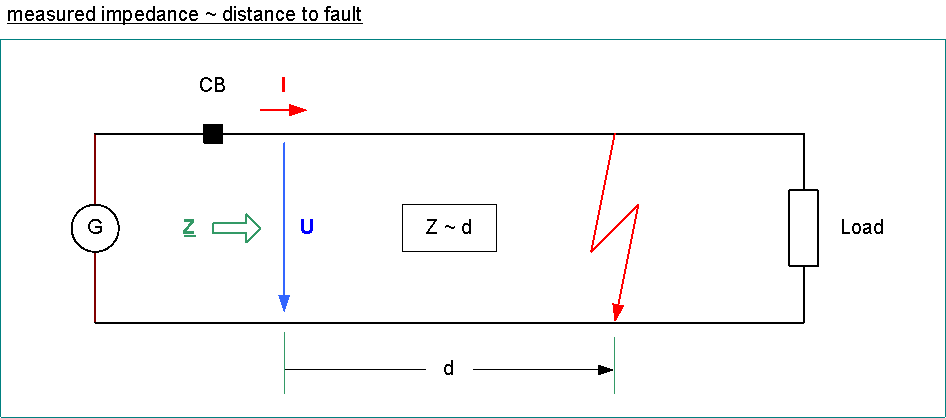
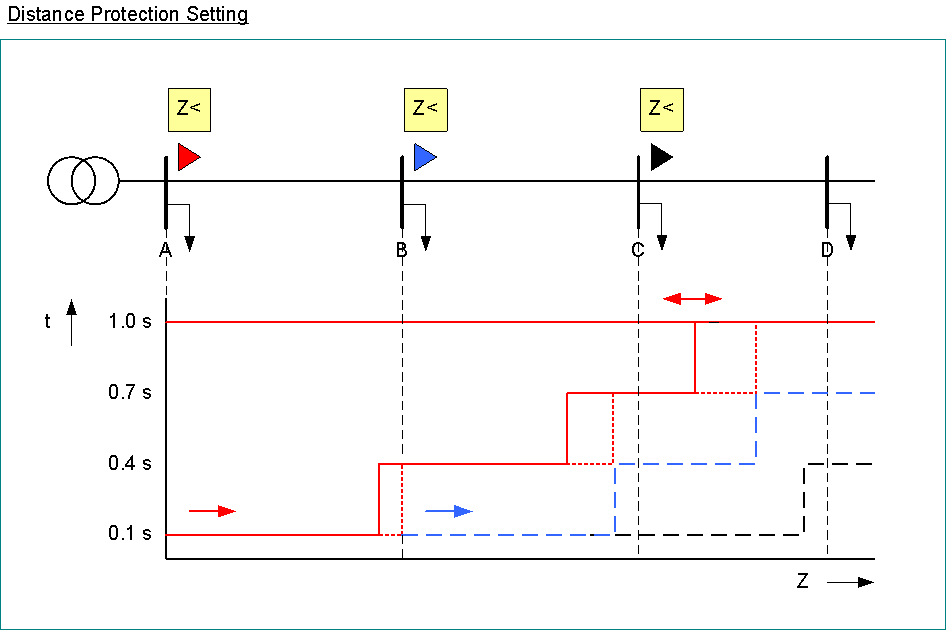
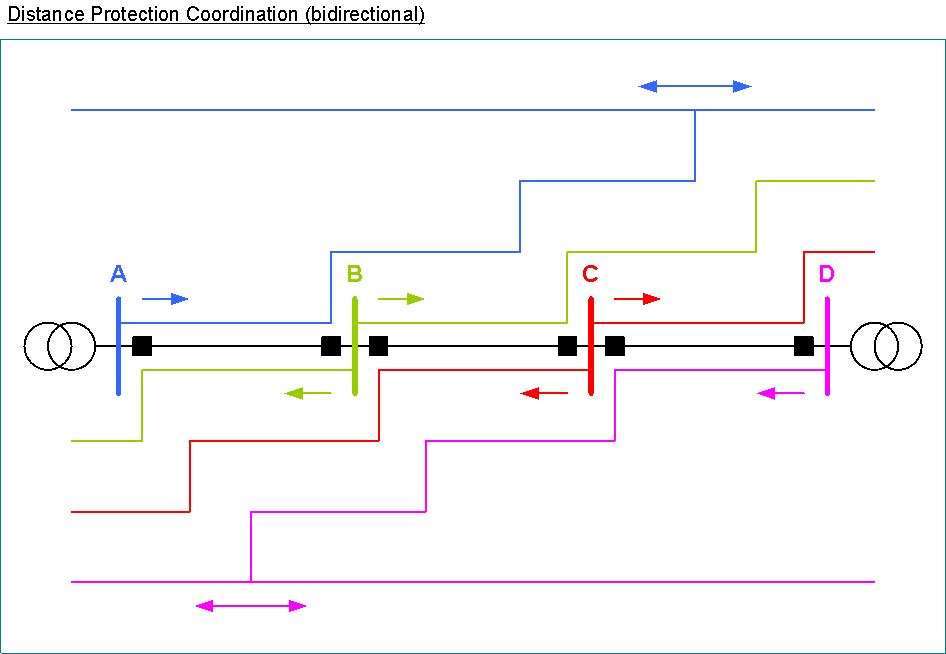
distance protection < Z
extra high voltage (EHV), high voltage (HV), medium voltage (MV)
current and voltage measured
impedance is determined form voltage and current
loop impedance is proportional to distance between the relay and the short circuit
circuit breaker receives tripping signal from distance relay
time steps
quick tripping, if impedance is in the lowest impedance zone
delayed tripping, if impedance is in higher impedance zone
=> backup protection, if relay closer to the fault fails
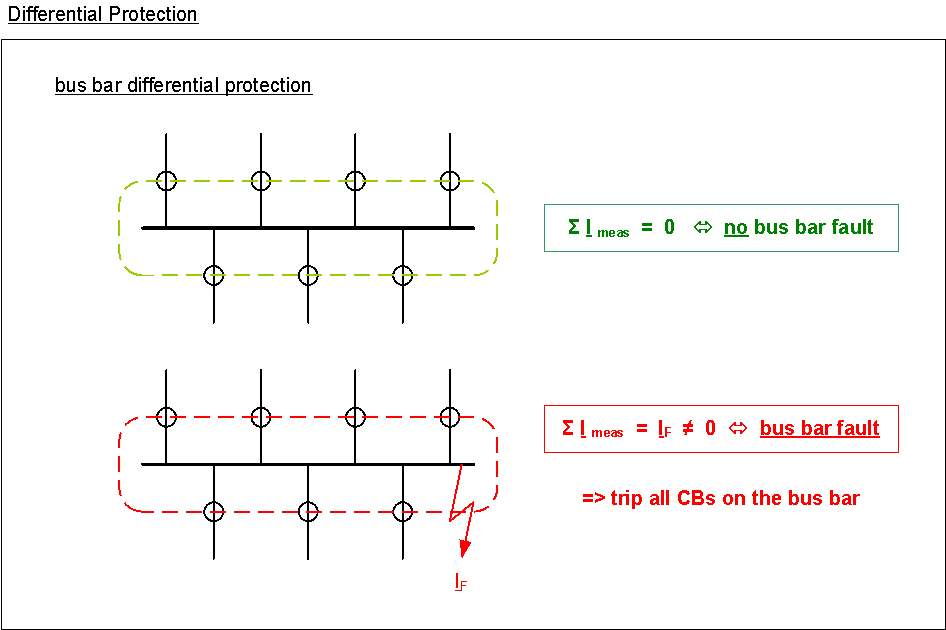
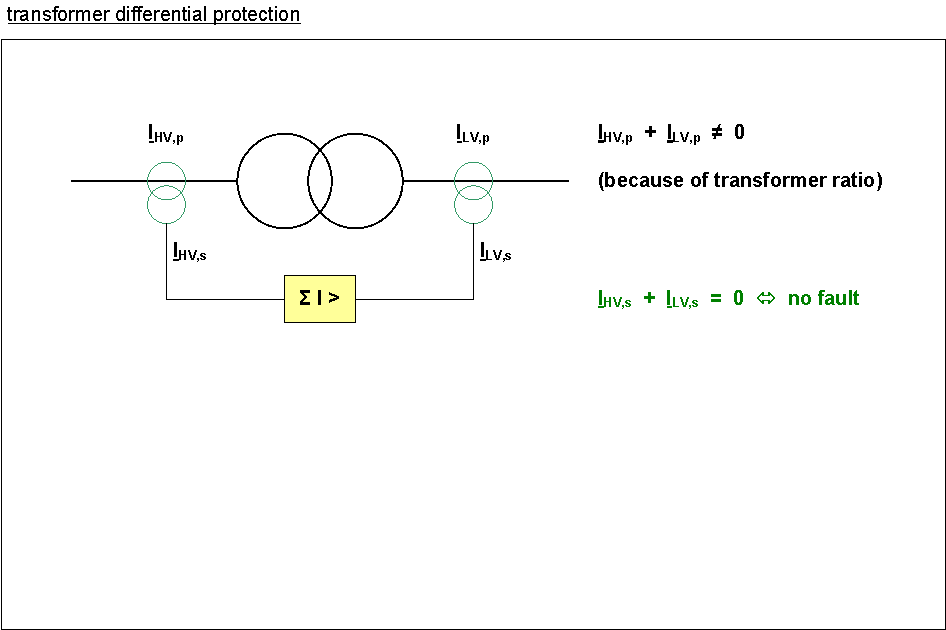
differential protection
used for bus bars, transformers, generators, (short lines)
total of incoming and outgoing currents must equal zero, deviation in case of a fault
transformers: currents different on primary and secondary side of the transformer
unified secondary current (1 or 5A) of current-transformer (instrument transformer)
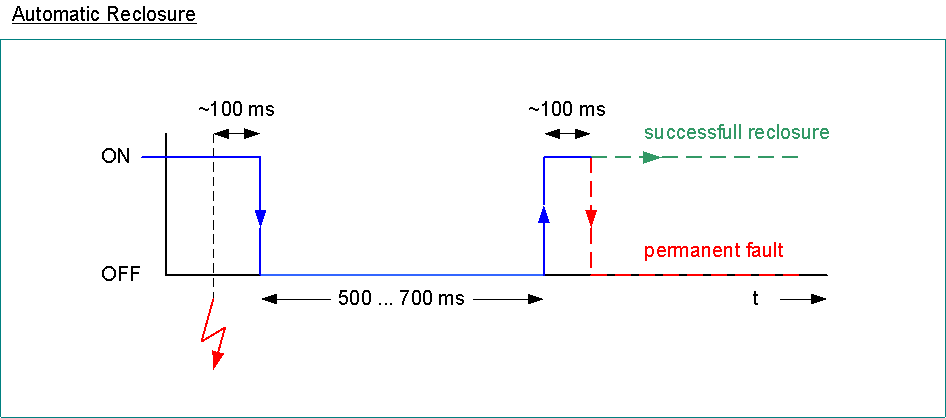
automatic reclosure (for overhead lines)
sequence of events
relay recognizes fault
circuit breaker trips after < 100 ms
automatic reclosure after 500...700 ms
if arc is extinguished in the meantime => successful reclosure
otherwise permanent fault => final tripping of the line after ~100 ms
n-1-security
(see slides in 2_Switching\Netzbetrieb_englisch.ppt)
n-1-criterion
system shall withstand single outage without expansion of the disturbance
HV, EHV
no influence on consumers for single fault
meshed network operations
redundancy
checked by loadflow calculations
outage simulation, contingency analysis
simulate each single outage, check for overloads and limit violations after line outages
avoid cascading: (overload) tripping of a line results in overloads of other lines
MV
open loops, not meshed
consumers interrupted for a limited time (30 min ... 2 h)
interruption tolerated for a limited period of time
possibility to restore supply by (manual) switching
if available, close sectioning switch
otherwise, bring mobile generator to the consumer site








